Thread Local Storage
Table of Contents
1. Thread Local Storage
使用 tls 主要有几种方式:
- 使用 __thread (gcc 扩展) 或 thread_local (c++11) 关键字.
- 使用 pthread
- 直接使用某个 tls slot, 例如 errno
它们对应不同的 tls slot. 具体的 tls 实现可以是 elf_tls 或 emutls, 前者使用 thread_pointer 寄存器保存 tls slot 的地址, 后者使用 emutls 模拟 thread_pointer
1.1. elf_tls
https://www.akkadia.org/drepper/tls.pdf
无论 elf_tls 还是 emutls 都需要解决几个问题:
- 如何找到 tls 初始化 image 并初始化 tls
- 如何确定某个 tls 变量的地址
- 如何分配 tls slot
对于 elf_tls, gcc 会生成 tls 相关信息 (例如 .tdata, .tbss, PT_TLS phdr, …) 保存在 elf 中,后续还需要 static linker, libc, pthread, runtime linker 等配合来使用 tls. 例如:
- libc 的 __libc_setup_tls 会把分配 tls 空间并用 .tdata 来初始化. pthread_create也需要执行类似的动作.
- tls 变量的地址在编译时会直接对应 tp 的偏移量
1.1.1. example
1.1.1.1. arm
#include <errno.h> __thread int xxx = 0xa; __thread int yyy = 0xb; __thread int zzz = 0xc; #define my_get_tls() ({ void** __val; __asm__("mrs %0, tpidr_el0" : "=r"(__val)); __val; }) int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { xxx = yyy + zzz; void** tls = my_get_tls(); printf("%p %p\n", &xxx, &tls[0]); return 0; }
$> aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc test.c -O0 -g3 -static $> aarch64-linux-gnu-objdump -D ./a.out 00000000000007f8 <main>: 7f8: d10043ff sub sp, sp, #0x10 7fc: b9000fe0 str w0, [sp,#12] 800: f90003e1 str x1, [sp] 804: d53bd040 mrs x0, tpidr_el0 808: 91400000 add x0, x0, #0x0, lsl #12 80c: 91005000 add x0, x0, #0x14 810: b9400001 ldr w1, [x0] 814: d53bd040 mrs x0, tpidr_el0 818: 91400000 add x0, x0, #0x0, lsl #12 81c: 91006000 add x0, x0, #0x18 820: b9400000 ldr w0, [x0] 824: 0b000021 add w1, w1, w0 828: d53bd040 mrs x0, tpidr_el0 82c: 91400000 add x0, x0, #0x0, lsl #12 830: 91004000 add x0, x0, #0x10 834: b9000001 str w1, [x0] // 这里没有使用 emutls, 而是通过 tpidr_el0 直接获得 tls 地址: // xxx 位于 tls[0x10] // yyy 位于 tls[0x14] // zzz 位于 tls[0x18] $> ./a.out 0x3eeeb700 0x3eeeb6f0 // 可见 &xxx = tls[0x10]
1.1.1.2. riscv
$> cat test.c
__thread int x = 0xa;
__thread int y = 0xb;
float foo(float k) {
int a = x;
int b = y;
}
$> /opt/riscv/bin/riscv64-unknown-linux-gnu-gcc test.c -O0 -nostdlib
$> /opt/riscv/bin/riscv64-unknown-linux-gnu-objdump -d ./a.out
0000000000010158 <foo>:
10158: 7179 addi sp,sp,-48
1015a: f422 sd s0,40(sp)
1015c: 1800 addi s0,sp,48
1015e: fca42e27 fsw fa0,-36(s0)
10162: 00022783 lw a5,0(tp) # 0 <x>
10166: fef42623 sw a5,-20(s0)
1016a: 00422783 lw a5,4(tp) # 4 <y>
1016e: fef42423 sw a5,-24(s0)
10172: 0001 nop
10174: f0078553 fmv.w.x fa0,a5
10178: 7422 ld s0,40(sp)
1017a: 6145 addi sp,sp,48
1017c: 8082 ret
riscv 使用 tp 做为 thread pointer, 直接通过 `0(tp), 4(tp)` 访问 `x, y`
1.1.2. dso
当 dso 中使用了 __thread 时, 情况会变得复杂, 因为链接 dso 时无法确定变量 (例如 extern int x) 相对 tp 的 offset, 类似于链接 dso 时无法确定普通变量的地址. 两者都需要通过 .got 处理: tls 对应的 .got 需要保存 rtld 分配的 tpoff, tls offset 以及某些回调函数, 普通变量的 .got 则保存着真实地址
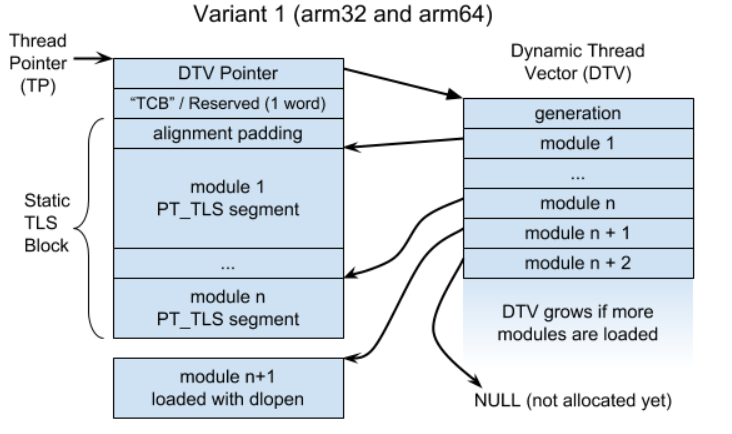
https://android.googlesource.com/platform/bionic/+/HEAD/docs/elf-tls.md
1.1.2.1. TLSDESC
aarch64 没有使用 __tls_get_addr, 它默认使用的 tls dialect 为 desc, 会通过 TLSDESC 类型的重定位类型支持 dso 使用 tls
测试程序:
void tls_hello() { failed_asserts++; }
重定位类型:
000000000005fa18 0000016e00000407 R_AARCH64_TLSDESC 0000000000000060 failed_asserts + 0
生成汇编:
0000000000037e30 <tls_hello>: 37e30: d53bd042 mrs x2, tpidr_el0 37e34: a9bf7bfd stp x29, x30, [sp, #-16]! // 0x5fa18 保存着一个类似于 __tls_get_addr 的函数, // 它的参数是 0x5fa18 本身, 调用后返回对应的 tls 数据地址的 offset 37e38: 910003fd mov x29, sp 37e3c: 90000140 adrp x0, 5f000 <vfs_unlink+0x286a0> 37e40: f9450c01 ldr x1, [x0, #2584] 37e44: 91286000 add x0, x0, #0xa18 37e48: d63f0020 blr x1 37e4c: b8606841 ldr w1, [x2, x0] 37e50: 11000421 add w1, w1, #0x1 37e54: b8206841 str w1, [x2, x0] 37e58: a8c17bfd ldp x29, x30, [sp], #16 37e5c: d65f03c0 ret
rtld 对应代码:
case R_AARCH64_TLSDESC: *r_ptr = (size_t)__tlsdesc_static; /* dest->tpoff 是当前 so 对应的 tls 偏移量, 这个信息需要在运行时由 rtld 确定 */ *(r_ptr + 1) = dest->tpoff + sym_addr + r_addend; break; /* ==================== */ void modules_process_tls(rtld_t *rtld){ list_foreach(rtld->modules, modules_link, module_t, m) { list_append(&m->imodules_link, &rtld->imodules); rtld->tls_align = max(rtld->tls_align, m->tls_align); rtld->tls_size = ALIGN_UP(rtld->tls_size, m->tls_align); /* so 对应的 tpoff 是前面加载的 so 的 tdata/tbss 累积的结果 */ m->tpoff = rtld->tls_size; rtld->tls_size += m->tdata_size + m->tbss_size; } }
FUNCTION_BEGIN(__tlsdesc_static) ldr x0,[x0,#8] ret FUNCTION_END(__tlsdesc_static)
1.1.2.2. __tls_get_addr
riscv 会使用 __tls_get_addr 确定 tls 的地址, 例如:
extern __thread int kkk; void foo() { kkk += 1; }
$> riscv-gcc test.c -O0 -g -fPIC -shared -o libtest.so $> riscv-objdump -d libtest.so --disassemble=foo 000000000000055a <foo>: 55a: 1101 addi sp,sp,-32 55c: ec06 sd ra,24(sp) 55e: e822 sd s0,16(sp) 560: e426 sd s1,8(sp) 562: 1000 addi s0,sp,32 564: 00002517 auipc a0,0x2 # __tls_get_addr 的参数是 1fd8 568: a7450513 addi a0,a0,-1420 # 1fd8 <kkk@Base> 56c: f55ff0ef jal 4c0 <__tls_get_addr@plt> 570: 87aa mv a5,a0 572: 439c lw a5,0(a5) 574: 2785 addiw a5,a5,1 576: 0007849b sext.w s1,a5 57a: 00002517 auipc a0,0x2 57e: a5e50513 addi a0,a0,-1442 # 1fd8 <kkk@Base> 582: f3fff0ef jal 4c0 <__tls_get_addr@plt> 586: 87aa mv a5,a0 588: c384 sw s1,0(a5) 58a: 0001 nop 58c: 60e2 ld ra,24(sp) 58e: 6442 ld s0,16(sp) 590: 64a2 ld s1,8(sp) 592: 6105 addi sp,sp,32 594: 8082 ret
Relocation section '.rela.dyn' at offset 0x3c8 contains 8 entries:
Offset Info Type Symbol's Value Symbol's Name + Addend
...
0000000000001fd8 0000000500000007 R_RISCV_TLS_DTPMOD64 0000000000000000 kkk + 0
0000000000001fe0 0000000500000009 R_RISCV_TLS_DTPREL64 0000000000000000 kkk + 0
...
musl 中对应的 rtld 代码:
#define REL_DTPMOD R_RISCV_TLS_DTPMOD64 #define REL_DTPOFF R_RISCV_TLS_DTPREL64 case REL_DTPMOD: /* 对应 rtld 动态分配的 dtv id, 通过 dtv[id] 可以得于 so 的 dtv */ *reloc_addr = def.dso->tls_id; break; case REL_DTPOFF: /* 对应相对 dtv 内部的 offset */ *reloc_addr = tls_val + addend - DTP_OFFSET; break;
void *__tls_get_addr(tls_mod_off_t *v) { pthread_t self = __pthread_self(); return (void *)(self->dtv[v[0]] + v[1]); }
可见 __tls_get_addr 的方式与 TLSDESC 基本相同, 不同之处在于:
- 前者的回调函数是固定的 __tls_get_addr, 后者写在重定位项里
- 前者通过重定位项保存了 tls_id, 需要通过 dtv[id] 获得 tpoff, 后者直接把 tpoff 写在重定位项中
- TLSDESC 不需要使用 dtv, 因为它直接使用重定位项中的 tpoff
1.1.2.3. dtv
__tls_get_addr 需要配合 dtv 工作, 因为它的参数是 tls_id, 对应 dtv 项. 新的 so 加载后会新建 dtv 项:
/* tls_id 是 so 加载后分配的 id, 是自增的 */ m = module_by_id(rtld, tls_id); tls_block = memalign(m->tls_align, m->tdata_size + m->tbss_size); memcpy(tls_block, m->tdata, m->tdata_size); memset(tls_block + m->tdata_size, 0, m->tbss_size); tcb->dtv[tls_id] = tls_block;
1.1.3. tls_model
通过 `gcc -ftls-model=xxx` 指定 tls_model, 常见的有:
- local-exec
- initial-exec
- global-dynamic
运行时性能依次降低, 但灵活性依次提高
1.1.3.1. local-exec
所有 tls 符号在静态链接时是确定的, 可以使用 local-exec.
__thread int xxx; void foo() { xxx += 1; } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { return 0; }
$> arm-gcc test.c -O0 -c
$> readelf -a test.o
Relocation section '.rela.text' at offset 0x44a8 contains 4 entries:
Offset Info Type Symbol's Value Symbol's Name + Addend
0000000000000004 0000001900000225 R_AARCH64_TLSLE_ADD_TPREL_HI12 0000000000000000 xxx + 0
0000000000000008 0000001900000227 R_AARCH64_TLSLE_ADD_TPREL_LO12_NC 0000000000000000 xxx + 0
0000000000000018 0000001900000225 R_AARCH64_TLSLE_ADD_TPREL_HI12 0000000000000000 xxx + 0
000000000000001c 0000001900000227 R_AARCH64_TLSLE_ADD_TPREL_LO12_NC 0000000000000000 xxx + 0
$> arm-objdump -dr test.o
Disassembly of section .text:
0000000000000000 <foo>:
0: d53bd040 mrs x0, tpidr_el0
4: 91400000 add x0, x0, #0x0, lsl #12
4: R_AARCH64_TLSLE_ADD_TPREL_HI12 xxx
8: 91000000 add x0, x0, #0x0
8: R_AARCH64_TLSLE_ADD_TPREL_LO12_NC xxx
c: b9400000 ldr w0, [x0]
10: 11000401 add w1, w0, #0x1
14: d53bd040 mrs x0, tpidr_el0
18: 91400000 add x0, x0, #0x0, lsl #12
18: R_AARCH64_TLSLE_ADD_TPREL_HI12 xxx
1c: 91000000 add x0, x0, #0x0
1c: R_AARCH64_TLSLE_ADD_TPREL_LO12_NC xxx
20: b9000001 str w1, [x0]
24: d503201f nop
28: d65f03c0 ret
$> arm-gcc test.c -O0
$> arm-objdump a.out --disassemble=foo
0000000000000754 <foo>:
754: d53bd040 mrs x0, tpidr_el0
758: 91400000 add x0, x0, #0x0, lsl #12
# ld 确定的 x 的 tls offset 为 0x10, 并 patch 到 .text
# 只所以是 0x10 (16) 而不是 0, 是因为 arm64 里 bfd 规定 tp+16 才对应 tls 数据
75c: 91004000 add x0, x0, #0x10
760: b9400000 ldr w0, [x0]
764: 11000401 add w1, w0, #0x1
768: d53bd040 mrs x0, tpidr_el0
76c: 91400000 add x0, x0, #0x0, lsl #12
770: 91004000 add x0, x0, #0x10
774: b9000001 str w1, [x0]
778: d503201f nop
77c: d65f03c0 ret
1.1.3.2. initial-exec
initial-exec 针对的是 initially loaded 的 dso, 即不是通过 dlopen 使用的 dso, 这些 dso 如果使用到其它 dso 或 executable 定义的 tls symbol, 则需要通过 got 保存那些 tls symbol 的 tls offset
extern __thread int xxx; void foo() { xxx += 1; }
$> arm-gcc test.c -O0 -c
$> readelf -r test.o
Relocation section '.rela.text' at offset 0x200 contains 4 entries:
Offset Info Type Symbol's Value Symbol's Name + Addend
0000000000000004 0000000b0000021d R_AARCH64_TLSIE_ADR_GOTTPREL_PAGE21 0000000000000000 xxx + 0
0000000000000008 0000000b0000021e R_AARCH64_TLSIE_LD64_GOTTPREL_LO12_NC 0000000000000000 xxx + 0
000000000000001c 0000000b0000021d R_AARCH64_TLSIE_ADR_GOTTPREL_PAGE21 0000000000000000 xxx + 0
0000000000000020 0000000b0000021e R_AARCH64_TLSIE_LD64_GOTTPREL_LO12_NC 0000000000000000 xxx + 0
$> arm-objdump -dr test.o
0000000000000000 <foo>:
0: d53bd041 mrs x1, tpidr_el0
4: 90000000 adrp x0, 0 <xxx>
4: R_AARCH64_TLSIE_ADR_GOTTPREL_PAGE21 xxx
# NOTE: R_AARCH64_TLSIE_ADR_GOTTPREL_PAGE21 这个重定位是给静态 linker 使用的, 用来定义 got 表项
8: f9400000 ldr x0, [x0]
8: R_AARCH64_TLSIE_LD64_GOTTPREL_LO12_NC xxx
c: 8b000020 add x0, x1, x0
10: b9400000 ldr w0, [x0]
14: 11000401 add w1, w0, #0x1
18: d53bd042 mrs x2, tpidr_el0
1c: 90000000 adrp x0, 0 <xxx>
1c: R_AARCH64_TLSIE_ADR_GOTTPREL_PAGE21 xxx
20: f9400000 ldr x0, [x0]
20: R_AARCH64_TLSIE_LD64_GOTTPREL_LO12_NC xxx
24: 8b000040 add x0, x2, x0
28: b9000001 str w1, [x0]
2c: d503201f nop
30: d65f03c0 ret
$> arm-gcc test.c -O0 -shared -o libtest.so
$> readelf -r libtest.so
Relocation section '.rela.dyn' at offset 0x350 contains 8 entries:
Offset Info Type Symbol's Value Symbol's Name + Addend
...
# NOTE: R_AARCH64_TLS_TPREL64 是 rtld 使用的, 为了在运行时获得 xxx 真正的 tlf offset
# 1ffc8 位于 got
# musl 中针对 R_AARCH64_TLS_TPREL64 的重定位代码为:
# *reloc_addr = tls_val + def.dso->tls.offset + TPOFF_K + addend;
# 其中 def.dso->tls.offset 是 dso 被 initially loaded 时分配的 offset
000000000001ffc8 0000000400000406 R_AARCH64_TLS_TPREL64 0000000000000000 xxx + 0
...
1.1.3.3. global-dynamic
global-dynamic 是最复杂也是最灵活的 tls model, 可以支持通过 dlopen 加载的 dso
__thread int xxx; void foo() { xxx += 1; }
$> arm-gcc test.c -O0 -c -fPIC
$> readelf -r test.o
Relocation section '.rela.text' at offset 0x258 contains 8 entries:
Offset Info Type Symbol's Value Symbol's Name + Addend
0000000000000008 0000000c00000232 R_AARCH64_TLSDESC_ADR_PAGE21 0000000000000000 xxx + 0
000000000000000c 0000000c00000233 R_AARCH64_TLSDESC_LD64_LO12 0000000000000000 xxx + 0
0000000000000010 0000000c00000234 R_AARCH64_TLSDESC_ADD_LO12 0000000000000000 xxx + 0
0000000000000014 0000000c00000239 R_AARCH64_TLSDESC_CALL 0000000000000000 xxx + 0
0000000000000028 0000000c00000232 R_AARCH64_TLSDESC_ADR_PAGE21 0000000000000000 xxx + 0
000000000000002c 0000000c00000233 R_AARCH64_TLSDESC_LD64_LO12 0000000000000000 xxx + 0
0000000000000030 0000000c00000234 R_AARCH64_TLSDESC_ADD_LO12 0000000000000000 xxx + 0
0000000000000034 0000000c00000239 R_AARCH64_TLSDESC_CALL 0000000000000000 xxx + 0
# NOTE: rela 重定位项的作用是生成 rtld 的重定位信息, 例如: rtld 重定位时里需要修改的 got 位置
$> arm-objdump -d test.o
0000000000000000 <foo>:
0: a9bf7bfd stp x29, x30, [sp, #-16]!
4: 910003fd mov x29, sp
8: 90000000 adrp x0, 0 <foo>
8: R_AARCH64_TLSDESC_ADR_PAGE21 xxx
c: f9400001 ldr x1, [x0]
c: R_AARCH64_TLSDESC_LD64_LO12 xxx
10: 91000000 add x0, x0, #0x0
10: R_AARCH64_TLSDESC_ADD_LO12 xxx
14: d63f0020 blr x1
14: R_AARCH64_TLSDESC_CALL xxx
18: d53bd041 mrs x1, tpidr_el0
1c: 8b000020 add x0, x1, x0
20: b9400000 ldr w0, [x0]
24: 11000401 add w1, w0, #0x1
28: 90000000 adrp x0, 0 <foo>
28: R_AARCH64_TLSDESC_ADR_PAGE21 xxx
2c: f9400002 ldr x2, [x0]
2c: R_AARCH64_TLSDESC_LD64_LO12 xxx
30: 91000000 add x0, x0, #0x0
30: R_AARCH64_TLSDESC_ADD_LO12 xxx
34: d63f0040 blr x2
34: R_AARCH64_TLSDESC_CALL xxx
38: d53bd042 mrs x2, tpidr_el0
3c: 8b000040 add x0, x2, x0
40: b9000001 str w1, [x0]
44: d503201f nop
48: a8c17bfd ldp x29, x30, [sp], #16
4c: d65f03c0 ret
$> arm-gcc test.c -O0 -fPIC -shared -o libtest.so
$> readelf -r libtest.so
Relocation section '.rela.plt' at offset 0x430 contains 3 entries:
Offset Info Type Symbol's Value Symbol's Name + Addend
...
# NOTE: 0x20010 位置 got
0000000000020010 0000000700000407 R_AARCH64_TLSDESC 0000000000000000 xxx + 0
...
# NOTE: R_AARCH64_TLSDESC 需要修改 0x20010 为一个回调函数的地址, 0x20018 为一个 tls_index 结构体的地址
# 这个 tls_index 需要包括一个 mod_id 和一个 tls_offset, mod_id 是 so 被加载后确定的唯一 id, tls_offset 是
# tls symbol 在 so 内部的 tls_offset.
# 回调函数会以这个 tls_index 做为参数, 在运行时创建 dso
# 对应的 dtv 项, 从 dtv[mod_id] 确定 so 对应的 tls 的 base 地址, 然后加上 tls_offset 可以得到最终的 tls offset
$> arm-objdump -d libtest.so
00000000000005d4 <foo>:
5d4: a9bf7bfd stp x29, x30, [sp, #-16]!
5d8: 910003fd mov x29, sp
# NOTE: 0x20000+#16=0x200010, 即 got 表项的地址
5dc: 90000100 adrp x0, 20000 <__cxa_finalize>
5e0: f9400801 ldr x1, [x0, #16]
5e4: 91004000 add x0, x0, #0x10
# NOTE: 0x200010 存储的是回调函数, blx 过去, 并以 0x200010 做为参数
# 回调函数需要从 0x200018 获得 tls_index
5e8: d63f0020 blr x1
5ec: d53bd041 mrs x1, tpidr_el0
5f0: 8b000020 add x0, x1, x0
5f4: b9400000 ldr w0, [x0]
5f8: 11000401 add w1, w0, #0x1
5fc: 90000100 adrp x0, 20000 <__cxa_finalize>
600: f9400802 ldr x2, [x0, #16]
604: 91004000 add x0, x0, #0x10
608: d63f0040 blr x2
60c: d53bd042 mrs x2, tpidr_el0
610: 8b000040 add x0, x2, x0
614: b9000001 str w1, [x0]
618: d503201f nop
61c: a8c17bfd ldp x29, x30, [sp], #16
620: d65f03c0 ret
在 riscv 实现 global-dynamic 使用的是 __tls_get_addr, 机制类似但不完全一样.
之所以需要通过回调函数实现 global-dynamic, 是因为 dso 被某个线程 dlopen 后, 虽然有可能在这时实现针对这个线程的重定位, 但并不存在类似于 inital-exec 时 `线程创建` 这样的时机可以让其它线程也完成重定位. 通过回调函数, 则可以让每个线程都可以按需进行重定位, 实际上, 可以大约这样实现这个回调函数:
__tls_dynamic(mod_id, local_offset):
if mod_id > size(__dtv):
__dtv[mod_id]=create_dtv()
return dtv[mod_id]+local_offset
1.1.3.4. 其它
一般不需要手动指定 tls_model, 因为 gcc 有一个隐含的规则:
- 使用了 `-fPIC`, 则会使用 global-dynamic
- 没使用 `-fPIC` 但使用了 `extern __thread xxx`, 则使用 initial-exec
- 没使用 `-fPIC` 且没有使用 `extern __thread xxx`, 则使用 local-exec
1.1.4. pthread_tls
由于 elf_tls 和 pthread_tls 都需要使用 thread_pointer, 为了避免两者冲突, 需要分配一下 tp 指向的内存, 一部分给 elf_tls, 一部分给 pthread_tls.
pthread_tls 的 specific 数据通过 `THREAD_SELF->specific` 访问, arm 和 riscv 的 `THREAD_SELF` 在 tp 的前面, 而 elf_tls 的数据在 tp 后面.
/* arm */ #define THREAD_SELF ((struct pthread *)__builtin_thread_pointer() - 1) /* riscv */ #define THREAD_SELF \ ((struct pthread \ *)(READ_THREAD_POINTER() - TLS_TCB_OFFSET - TLS_PRE_TCB_SIZE))
ps. arm 的 xxx 在 tp[0x10] 而 riscv 的 x 在 tp[0], 这个 offset 取决于 bfd 的 `tpoff` 函数
Backlinks
Linker Relaxation (Linker Relaxation): 1. 如果 symbol 在 .tdata 中, 使用 tp 做基址寄存器, 以支持 elf_tls
1.2. emutls
__thread int xxx = 0xa; void foo() { printf("%d\n", xxx); }
gcc 编译以上代码时, 会生成几个特殊的符号:
- __emutls_t.xxx
- __emutls_v.xxx
这些符号的作用是定位 xxx 在 tls 中的位置(和初值), 然后再通过 __emutls_get_address 拿到 tls 数据
$> aarch64-linux-android-gcc foo.c -fPIC -shared -o libfoo.so -O0 -g3 $> nm libfoo.so|grep xxx 0000000000000d24 r __emutls_t.xxx 0000000000012008 D __emutls_v.xxx // 其中 __emutls_v.xxx 位于 .data, __emutls_t.xxx 位于 .rodata
1.2.1. __emutls_v
__emutls_v 的类型是 __emutls_control:
typedef struct __emutls_control { size_t size; /* size of the object in bytes */ size_t align; /* alignment of the object in bytes */ union { uintptr_t index; /* data[index-1] is the object address */ void* address; /* object address, when in single thread env */ } object; void* value; /* null or non-zero initial value for the object */ } __emutls_control;
index
__emutls_control 是所有线程都会访问的一个数据结构, 它所保存的 index 标识了 xxx 在各个线程的 emutls array 中的索引
value
若 xxx 有初值, 则存在一个 __emutls_t.xxx 符号, 保存着这个初值. loader 会负责把 value 指向这个 __emutls_t.xxx
__emutls_v.xxx 相当于 xxx 登记的全局标识, 所有线程和代码都需要先定位到__emutls_v.xxx 后, 然后根据 __emutls_t.xxx.object.index 在各自的 emutls array 中找到 xxx 真正的 tls 地址
1.2.2. __emutls_t
__emutls_t.xxx 保存着 xxx 的初值
1.2.3. example
$> objdump -D libfoo.so
0000000000000a4c <foo>:
a4c: a9bf7bfd stp x29, x30, [sp,#-16]!
a50: 910003fd mov x29, sp
a54: b0000080 adrp x0, 11000 <__emutls_t.xxx+0x102dc>
a58: f947fc00 ldr x0, [x0,#4088]
a5c: 9400004d bl b90 <__emutls_get_address>
a60: b9400001 ldr w1, [x0]
// [11000,#4088] ([0x11ff8]) 保存的是 __emutls_v.xxx 对应的 GOT entry:
Disassembly of section .got:
0000000000011f50 <.got>:
...
11f68: 000008f0 .word 0x000008f0
...
11ff8: 00012008 .word 0x00012008
...
0000000000012008 <__emutls_v.xxx>:
12008: 00000004 .word 0x00000004
1200c: 00000000 .word 0x00000000
12010: 00000004 .word 0x00000004
...
// __emutls_v.xxx 的 index 初始为 0, value 也为 NULL, value 由 linker 负责初始化为对应的 __emutls_t.xxx,
// 而 index 是 emutls 代码在运行时运行赋值的
$> readelf -a ./libfoo.so
Relocation section '.rela.dyn' at offset 0x708 contains 4 entries:
...
000000012020 000000000403 R_AARCH64_RELATIV d24
...
// 0x12020 = 0x12008 + 24, 因为 offsetof(__emutls_v.xxx, value) = 24
Disassembly of section .rodata:
...
0000000000000d24 <__emutls_t.xxx>:
d24: 0000000a .word 0x0000000a
1.3. android tls
android 使用 emutls, 但 emutls 底层还是会使用 thread pointer 寄存器 (tpidr_el0), 而不是用模拟的方式.
+-----------------+
thread_pointer ---> | slot_self |
+-----------------+ +-----------------+
| slot_pthread_id | ---> | key_emutls | <--- emutls
+-----------------+ +-----------------+
| slot_errno | | key_xxx | <--- pthread_tls
+-----------------+ +-----------------+
| ... | | ... |
+-----------------+ +-----------------+
1.3.1. tls slot
tls 会指向一块和线程相关的内存, 这块内存相当于一个 `void *[N]`, 称为 tls_slot, slot 中的每个指针指向不同的 buffer, 常用的 slot 有:
SLOT_SELF
elf_tls 使用这个 slot
SLOT_THREAD_ID
pthread_tls 使用这个 slot
SLOT_ERRNO
errno 使用这个 slot
1.3.2. emutls
android toolchain 使用 emutls 来支持 `__thread` 关键字. 但它并非模拟的, 而是使用真实的 thread_pointer. gcc 的 emutls 实现在 libgcc 中, clang 的实现在 libcompiler_rt
emutls 使用 pthread_tls 实现. emutls 底层对应 pthread_tls 的一个 key
#include <errno.h> __thread int xxx = 1; __thread int yyy = 1; __thread int zzz = 1; int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { xxx = yyy + zzz; return 0; }
$> aarch64-linux-android-gcc test.c -O0 -g3 -fPIE -pie $> aarch64-linux-android-objdump -D ./a.out 0000000000000be8 <main>: be8: a9bd7bfd stp x29, x30, [sp,#-48]! bec: 910003fd mov x29, sp bf0: f9000bf3 str x19, [sp,#16] bf4: b9002fa0 str w0, [x29,#44] bf8: f90013a1 str x1, [x29,#32] bfc: d0000080 adrp x0, 12000 <__dso_handle> c00: 9100a000 add x0, x0, #0x28 c04: 94000055 bl d58 <__emutls_get_address> c08: b9400013 ldr w19, [x0] c0c: d0000080 adrp x0, 12000 <__dso_handle> c10: 91002000 add x0, x0, #0x8 c14: 94000051 bl d58 <__emutls_get_address> c18: b9400000 ldr w0, [x0] c1c: 0b000273 add w19, w19, w0 c20: d0000080 adrp x0, 12000 <__dso_handle> c24: 91012000 add x0, x0, #0x48 c28: 9400004c bl d58 <__emutls_get_address> c2c: b9000013 str w19, [x0] // 其中 __emutls_get_address 表示使用了 libgcc 提供的 emutls
1.3.2.1. __emutls_get_address
libcompiler_rt::emutls.c void* __emutls_get_address(__emutls_control* control) uintptr_t index = emutls_get_index(control); emutls_address_array* array = emutls_get_address_array(index); emutls_address_array* array = pthread_getspecific(emutls_pthread_key); return array->data[index - 1]; static void emutls_init(void): pthread_key_create(&emutls_pthread_key, emutls_key_destructor)
可见 android 的 emutls 是依赖 pthread_tls 来实现的.
1.3.3. pthread_tls
pthread 要求用户使用 pthread_key_create, pthread_get_specific 等 api 来设置 tls.
在 bionic 的实现中, pthread_tls 使用 tls_slot[1] 来实现. 在 glibc 中, 也是类似的实现.
pthread_getspecific(pthread_key_t key): pthread_key_data_t* data = &(__get_thread()->key_data[key]); return data->data; pthread_internal_t* __get_thread(): return reinterpret_cast<pthread_internal_t*>(__get_tls()[TLS_SLOT_THREAD_ID]); enum { TLS_SLOT_SELF = 0, // The kernel requires this specific slot for x86. TLS_SLOT_THREAD_ID, TLS_SLOT_ERRNO, // ... } #define __get_tls() ({ void** __val; __asm__("mrs %0, tpidr_el0" : "=r"(__val)); __val; })
pthread_tls 最终会使用 thread pointer: arm 的 thread pointer 是 tpidr_el0
1.3.4. errno
error 是使用 tls 实现的: 它使用一个单独的 pthread_tls slot
#define errno (*__errno()) volatile int* __errno() { return reinterpret_cast<int*>(&(__get_tls()[TLS_SLOT_ERRNO])); }
Backlinks
RISC-V Tutorial (RISC-V Tutorial > RISC-V Assembly > Register): - tp 是 thread pointer, 用来实现 Thread Local Storage
Retargeting GCC To RISC-V (Retargeting GCC To RISC-V > newlib/glibc > tls 相关): riscv 使用 tp (x4) 做 thread pointer, libc 中和 tls (Thread Local Storage) 相关 的代码需要考虑
